Cobalt 57, 58, 60 (57Co, 58Co, 60Co)
January 12, 2024
Although sold through the same channels as radiopharmaceuticals, molecules labeled with cobalt radioisotopes are not used for imaging, but for ex vivo diagnostics. Very small amounts of radiolabeled compounds are injected into patients and organic fluids (e.g., blood and urine samples) are taken at regular intervals for measurements of the function (metabolism) of some tissues or organs. The injected amounts are in the range of the microcurie (µCi), i.e., more than a thousand times lower than an imaging dose. As a consequence, the potential impact on the patient is not visible, neither is the impact on waste treatment. The doses are so small that the logistics of these products is not impacted by the transport regulation. The containers (usually simple covers sent by normal post) still have to bear the radioactivity logo, although the risk linked to potential contamination is close to zero. This material is considered similarly to diagnostic reagent despite their use as injected solution. They should be described and developed in diagnostic technology evaluation documents. The most important ones are summarized below but the associated tracers are not described in the reagent chapter, as they are not imaging or therapeutic agents.
Properties:
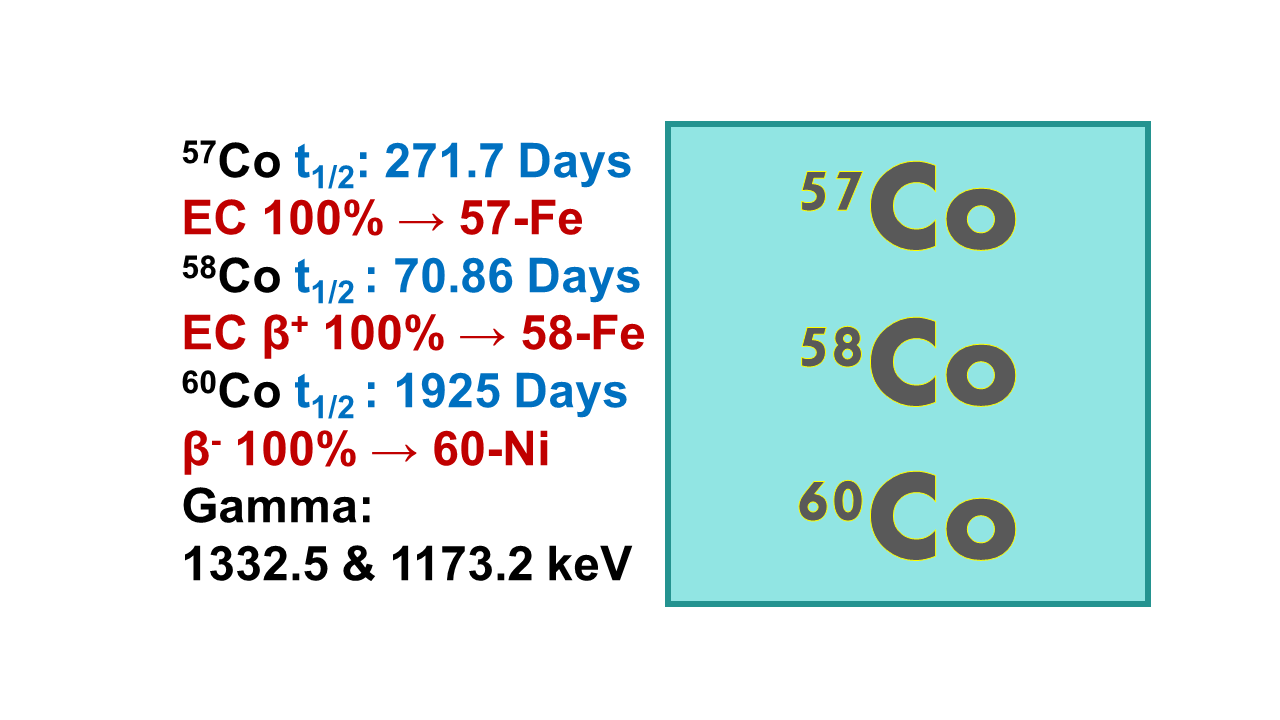
Cobalt-57 (57Co): half-life 271.8d, beta emitter at 699 keV (100%), gamma emitter at 122 keV (85%) and 136 keV (11%).
Cobalt-58 (58Co): half-life 70.9d, beta emitter at 1496 keV (84%) and at 474 keV (15%), positron emitter at 810 keV (99%).
Cobalt-60 (60Co): half-life 5.27y, beta emitter at 318 keV (100%), gamma emitter at 1,332 keV (99%). The interest in production of high amounts of 60Co is almost exclusively linked to its application as radioactive source for external radiotherapy (cobaltotherapy).
Manufacturing, source and availability:
All cobalt isotopes are produced by neutron activation in a reactor:
◼ 57Co: [58Ni(n,np)57Co] or [58Ni(n,2n)57Ni→57Co]. 57Co can also be produced in a cyclotron through the sequences [56Fe(d,n)57Co], at 8 MeV [natNi(p,2n)57Co] at 22 MeV or [59Co(p,3n)57Ni→57Co] at 40 MeV.
◼ 58Co: [58Ni(n,p)58Co].
◼ 60Co: [59Co(n,γ)60Co]; this irradiation process needs a period of 1,200 days. 60Co production sites include: Bruce-B., Pickering-A and -B and Gentilly-2 in Canada; Embalse in Argentina; Qinshan Phase III units 1 and 2 in China; Wolsong 1 and 2 in South Korea; PARR-1/KANUPP reactor from Pinstech, Islamabad, Pakistan; FSUE PA Mayak in Ozersk, JSC SSC RIAR in Dimitrovgrad, and Leningrad 1 in Russia (RBMK). India also has a source in Kota (BRIT) from the Rajasthan Atomic Power Project Cobalt Facility (RAPPCOF). In October 2019, Nordion announced an agreement with the Romanian company SNN (Romania’s national nuclear electricity producer) for the production of 60Co at the Cernavoda Nuclear Power plant.
Derivatives and applications:
Radioactive cobalt (57Co or 58Co) allows the radiolabeling of vitamin B12 for application in the Schilling test. The Schilling test is a medical investigation used for patients with vitamin B12 deficiency which helps to determine whether the patient has pernicious anemia. GE Healthcare Amersham has 57Co-labeled cyanocobalamine in its catalogue. 57Co-cyanocobalamine from Bracco (Rubratope-57, Dicopac) was withdrawn from the market.
60Co was mainly used as a source of irradiation, but interest in it is strongly declining for this application, with the exception of 60Co in high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy.
Price:
The price of pure cobalt isotope (when bought bulk) remains below EUR 1,000 (US$ 1,300) per mCi depending on the amount and quality. Usually, labeled compounds are sold as the final product at much lower radioactive amounts.
Between 2016 and 2018 and following the acquisition of Nordion, Sterigenics (renamed Sotera Health) increased the price of cobalt by more than 30%. As a consequence, new customers of external radiotherapy tend to prefer electronically generated gamma or X-ray beams, reducing even more the interest for 60Co.
Comments:
Due to their long half-lives, the cobalt isotopes cannot be used in imaging or therapeutic medical applications in the future, with the exception of 60Co in HDR brachytherapy. Cobalt-55 (55Co) and Cobalt-58m (58mCo) raised also some interest, but the applications must be considered as anecdotic.