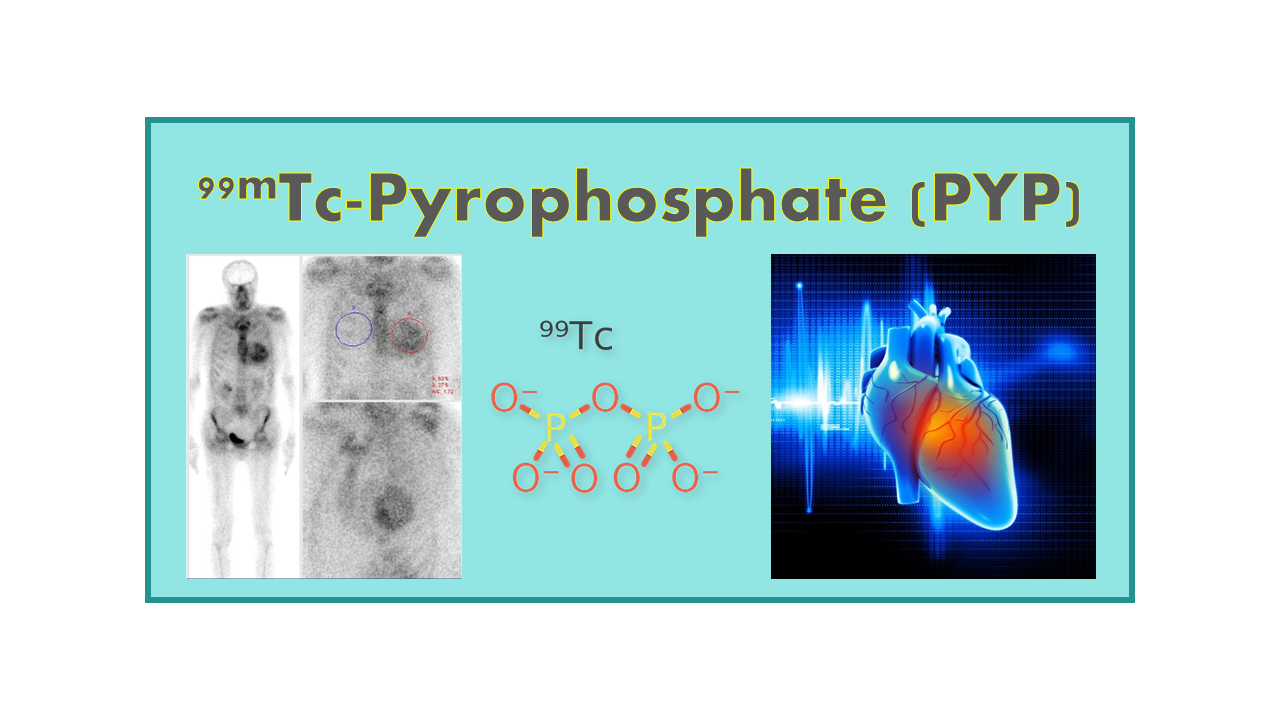
99mTc-Pyrophosphate (PYP)
April 29, 2024
99mTc-Pyrophosphate is a radiopharmaceutical used in nuclear medicine for both myocardial and bone imaging. It is a complex of the radioisotope technetium-99m (99mTc) and pyrophosphate, a compound that has an affinity for calcium ions.
In myocardial imaging, 99mTc-Pyrophosphate is used to detect areas of myocardial infarction, or heart attack. When there is damage to the heart muscle, calcium ions accumulate in the affected area. 99mTc-Pyrophosphate binds to these calcium ions, allowing for the visualization of the damaged tissue on a gamma camera.
In bone imaging, 99mTc-Pyrophosphate is used to detect bone lesions such as fractures, infections, and tumors. The radiopharmaceutical is taken up by areas of increased bone turnover, where it accumulates and emits gamma rays that can be detected by a gamma camera.
Overall, 99mTc-Pyrophosphate is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of various cardiac and skeletal conditions. It provides important information about the function and structure of the heart and bones, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions about patient care.
Description
99mTc-Pyrophosphate (99mTc-PYP, 99mTc-Stannous Pyrophosphate) is a generic 99mTc-labeled molecule used as a myocardial imaging agent and as a bone imaging agent.
Clinical applications
99mTc-Pyrophosphate is a myocardial perfusion imaging agent, useful in detection of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Dose per patient is in the range 5–20 mCi. Myocardial uptake of the tracer is often seen within 10 to 12 hours after infarction and becomes maximal between 24 to 72 hours post event. The scan may remain very positive for up to 6 days. This product has also some applications in the in vivo labeling of red blood cells for gated blood pool imaging and the detection of sites of gastrointestinal bleeding. It also found some applications as a bone imaging agent to delineate areas of altered osteogenesis.
Availability
The Pyrophosphate kits are sold under the names Amerscan PYP (GE Healthcare), Angiocis® (IBA Molecular – Curium; EU MA 1999), CIS Pyro (CIS bio; marketed since 1987), Pirfotech (DiaMed, Russian MA obtained in 1985), PYP (Pars Isotope), Pyrophosphate kit (Pharmalucence), Pyroscint (Medi-Radiopharma), TCK-38 (BRIT), Techne® Pyrophosphate (Fuji Film), Technescan® PYP (Mallinckrodt; marketed since 1974 in the US, since 1989 in EU; EU MA 2003) and Wuxi Jiangyuan.
Products withdrawn from the market include Hematocis (CISbio – red blood cell labeling; marketed since 1983, EU MA 1997, discontinued 2003), Phosphotec (BMS and Bracco), Pyrolite (CIS). Technescan Pyrophosphate (Mallinckrodt) was withdrawn from the US market in 2009.
In 2020 in the USA, a dose of Pyrophosphate is charged around US$ 60.
Competition
99mTc-PYP was a kind of precursor for cardiac imaging. It is used less commonly today because of the improved enzymatic detection methods for MI. Several proprietary compounds were developed in this field. Two of them (Sestamibi and Tetrofosmin) took almost 90% of the market for myocardial perfusion imaging agents.
New PET approaches including 15O-Water, 13N-Ammonia and 82Rb-Chloride are available while a couple of 18F-labeled compounds are now under development in this indication.
Comments
99mTc-PYP is an older generic product that has very limited chance of survival among all the new proprietary (and generic) approaches in myocardial perfusion imaging. There is also a lot of competition with blood pool imaging agents as well as with bone imaging agents.