169Er-Erbium Citrate
December 27, 2024
What is 169Er-Erbium Citrate?
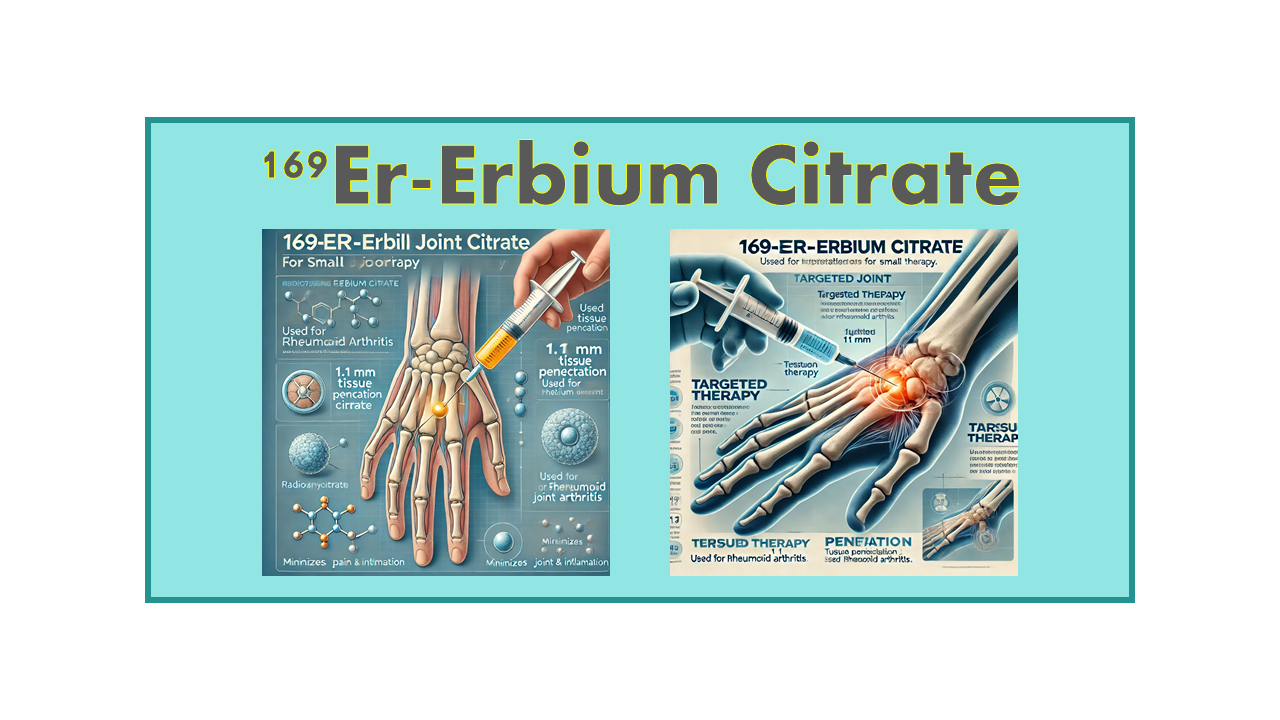
169Er-Erbium Citrate is a specialized radiopharmaceutical therapy designed for isotopic radiation synovectomy, particularly targeting small joints such as those in the hands and feet. This treatment leverages the therapeutic benefits of radioactive isotopes to alleviate symptoms of joint-related conditions.
Clinical Applications of 169Er-Erbium Citrate
This therapy is primarily used for managing rheumatoid mono- or oligo-arthritis in cases where:
- Intra-articular corticosteroid therapy has failed, or
- Corticosteroid therapy is contraindicated for the patient.
How it Works:
The suspension is administered directly into each painful joint. To ensure the therapy’s efficacy, the joint is immobilized for several hours or even days, minimizing the risk of radioactive substance escaping from the treated joint. Controlling the escape of the radioactive material is a critical aspect of this treatment, and advancements have made this issue highly manageable.
Tissue Penetration
The maximum tissue penetration for 169Er in radiosynoviorthesis is estimated to be 1.1 mm, making it particularly suitable for small-joint applications.
Availability
169Er-Erbium Citrate is commercially available through IBA Molecular (Curium) under the product code ERMM-1.
Competitive Landscape
Alternative Radiosynovectomy Technologies:
Several radionuclides have been developed to address joint-related issues through local irradiation. The options are tailored to joint size and beta radiation energy levels:
- 169Er: Designed for small joints such as hands and feet.
- 186Re: Suitable for mid-sized joints like wrists and ankles.
- 90Y: Effective for larger joints, including knees.
Other radionuclides such as 165Dy, 166Ho, and 153Sm have been researched but failed to achieve significant development. 188Re has shown promise, albeit with limited uptake by rheumatologists.
Emerging Technologies:
- Exubrion has introduced a veterinary formulation using particles loaded with 117mSn and is currently expanding its development for human applications.
Geographic Trends:
Radiosynovectomy has gained traction in German-speaking countries, where it is more widely available and reimbursed. However, the therapy faces competition from non-radioactive treatments that are more accessible to rheumatologists.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Key Challenges:
- Limited Supply: There is already a noticeable supply issue with 169Er, which could significantly affect its availability.
- Specialized Environment Requirements: The treatment necessitates a nuclear medicine physician trained in this therapy. This limits its application since referring rheumatologists often prefer non-radioactive alternatives that can be administered through routine weekly injections.
Growth Potential:
With strategic investment in promotion and the development of newer treatment protocols, 169Er-Erbium Citrate could witness broader adoption. Expanding physician training and improving supply chains will also be critical to its success.
Conclusion
169Er-Erbium Citrate has proven to be an effective therapy for small-joint arthritis through years of clinical application. However, its reliance on specialized environments and supply constraints present challenges. Efforts to address these limitations, combined with enhanced marketing, could pave the way for its expanded use in the global market.